Malecot's method of coancestry
Malecot's coancestry coefficient,  , refers to an indirect measure of genetic similarity of two individuals which was initially devised by the French mathematician Gustave Malécot.
, refers to an indirect measure of genetic similarity of two individuals which was initially devised by the French mathematician Gustave Malécot.
 is defined as the probability that any two alleles, sampled at random (one from each individual), are identical copies of an ancestral allele. In species with well-known lineages (such as domesticated crops),
is defined as the probability that any two alleles, sampled at random (one from each individual), are identical copies of an ancestral allele. In species with well-known lineages (such as domesticated crops),  can be calculated by examining detailed pedigree records. Modernly,
can be calculated by examining detailed pedigree records. Modernly,  can be estimated using genetic marker data.
can be estimated using genetic marker data.
Evolution of inbreeding coefficient in finite size populations
In a finite size population, after some generations, all individuals will have a common ancestor : 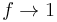 . Consider a non-sexual population of fixed size
. Consider a non-sexual population of fixed size 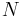 , and call
, and call 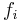 the inbreeding coefficient of generation
the inbreeding coefficient of generation 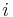 . Here,
. Here,  means the probability that two individuals picked at random will have a common ancestor. At each generation, each individual produces a large number
means the probability that two individuals picked at random will have a common ancestor. At each generation, each individual produces a large number 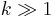 of descendants, from the pool of which
of descendants, from the pool of which 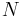 individual will be chosen at random to form the new generation.
individual will be chosen at random to form the new generation.
At generation  , the probability that two individuals have a common ancestor is "they have a common parent" OR "they descend from two distinct individuals which have a common ancestor" :
, the probability that two individuals have a common ancestor is "they have a common parent" OR "they descend from two distinct individuals which have a common ancestor" :
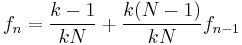
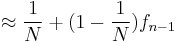
This is a recurrence relation easily solved. Considering the worst case where at generation zero, no two individuals have a common ancestor, 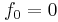 , we get
, we get
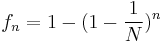
the scale of the fixation time (average number of generation it takes to homogenize the population) is therefore
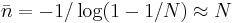
This computation trivially extends to the inbreeding coefficients of alleles in a sexual population by changing 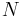 to
to 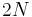 (the number a gametes).
(the number a gametes).
References
- Malécot G. Les mathématiques de l'hérédité. Paris: Masson & Cie, 1948.